Glucose homeostasis is regulated by insulin and glucagon, which are hormones secreted from pancreas. When the concentration of glucose in the blood increases, insulin is secreted to the blood to move glucose in the blood into liver and muscle cells, lowering blood sugar to the normal range. Parts of glucose which was moved from the blood to tissue are used as calorie source and the remains are stored in the glycogen or fat. On the contrary, when blood sugar falls under the normal range, glucagon is secreted from the pancreas to break down glucagon in the liver to produce glucose, maintaining the concentration of glucose in the blood to the normal range.
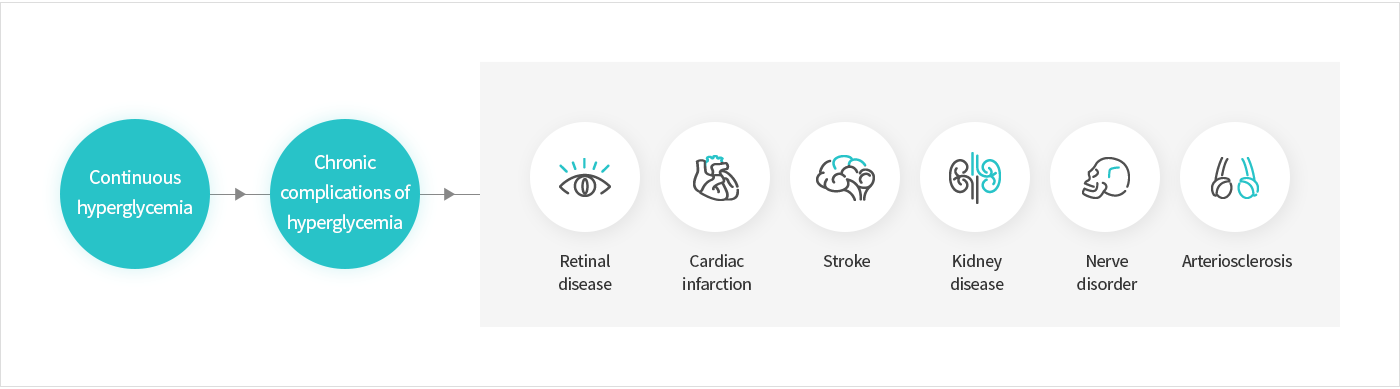
Diabetes literally means that sugar is released the urine. It means pathosis which blood sugar becomes higher than the normal range and it is overflowed with urine. However, as researches on pathophysiology of diabetes are conducted, it refers to all pathosis which blood sugar is maintained at higher level than normal state due to the breakdown of glucose homeostasis. The reason why the glucose homeostasis is not maintained for diabetics is because insulin is not sufficient and glucose in the blood can’t move into the cells due to the resistance to its function. As such, if glucose which should be used inside our body is not used properly and high blood sugar state is maintained for a long time, it may cause various complications.